Config API
JamLib comes with an easy to use config API that:
- Uses JSON5 - comments are added to the config file with descriptions, and user defined comments are preserved between saves thanks to Jankson.
- Automatically creates and registers (with ModMenu and Forge's config screen API) config screens which can also validate their inputs and prevent users from leaving if the config is invalid.
- Is easy to use.
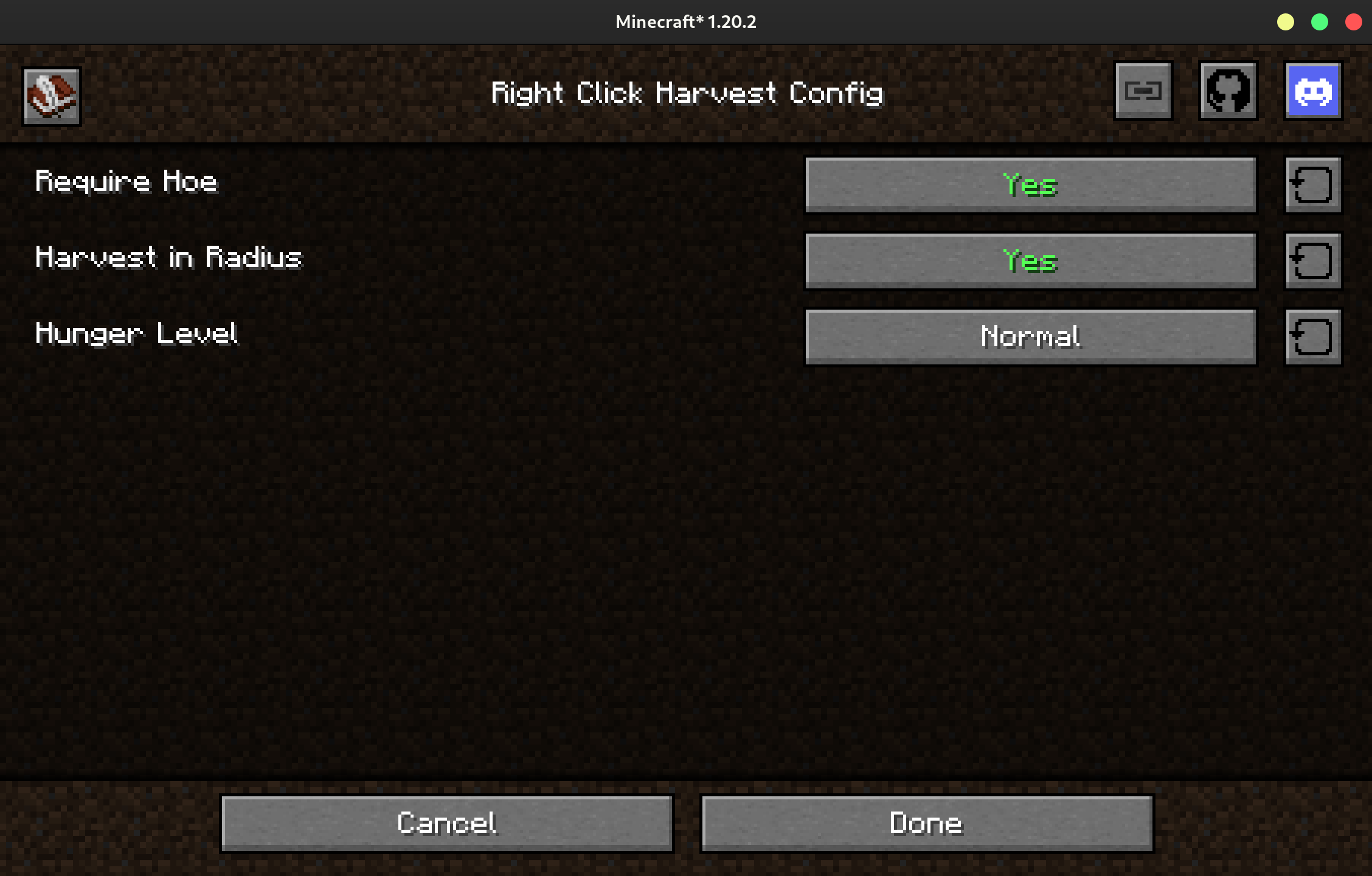
{
// - default: true (1)
"requireHoe": true,
// - default: true
"harvestInRadius": true,
/* - default: NORMAL
- must be one of: NONE, LOW, NORMAL, HIGH (2)
*/
"hungerLevel": "NORMAL"
}
- All of the comments here are automatically generated by JamLib.
- This is an enum field.
Getting Started
Once JamLib is added to your project, making a config is easy.
public class Config {
public boolean requireHoe = false; // (1)
public int rollTimes = 3; // (2)
public List<Integer> listOfInts = new ArrayList<>(List.of(1, 2, 3)); // (3)
}
- Config fields should be
public, notstatic, and notfinal. - The default value for this field is
3. This will be used when making a new config or when this field is added to an old config. - Lists are supported, but make sure that the default value is mutable - an
ArrayListis a safe bet.
public class YourModInit { // (1)
public static final ConfigManager<Config> CONFIG = new ConfigManager<>(MOD_ID, Config.class); // (2)
public static void configExample() { // (3)
System.out.println("Requires hoe: " + CONFIG.get().requireHoe); // (4)
CONFIG.get().rollTimes = 4; // (5)
CONFIG.save();
}
}
- The name and location of this class depends on your chosen mod loader. In Architectury, configs can be initialized in the common subproject.
- The
ConfigManageris responsible for saving and loading your config. When you create a manager, config screens are automatically registered using ModMenu (on Fabric and Quilt), and Forge's config screen API (on Forge). - You can access the config any time after the static initialization of your mod initializer.
- NEVER store the result of
ConfigManager#get(), as your stored value will not update when the config updates. - You can also programmatically update the config, just remember to call
ConfigManager#save()soon afterwards.
You'll also need to add translation keys to your language files:
{
// the rest of your language file
"config.testmod.testmod.title": "First config", // (1)
"config.testmod.second_config.title": "Second config", // (2)
"config.testmod.second_config.tooltip": "Tooltip for the second config on the selection screen", // (3)
"config.testmod.testmod.testBoolean": "Test boolean", // (4)
"config.testmod.testmod.testBoolean.tooltip": "Tooltip for the test config boolean",
"config.testmod.testmod.testEnum.first": "First", // (5)
"config.testmod.testmod.testEnum.second": "Second"
}
- If you only have one config file (as described above), the key is in the form
config.mod_id.mod_id.title. The title defaults to the mods name, as provided by the mod loader. - If you have multiple configs, as described below, the key is in the form
config.mod_id.config_name.title. - This tooltip is shown on the config selection screen if you have multiple configs.
- Field keys are in the form
config.mod_id.config_name.field_name. - Enum variants can be translated too, using their lowercase name.
More Advanced Usage
Built-in Annotations
JamLib comes with a few built-in annotations to enhance your configs.
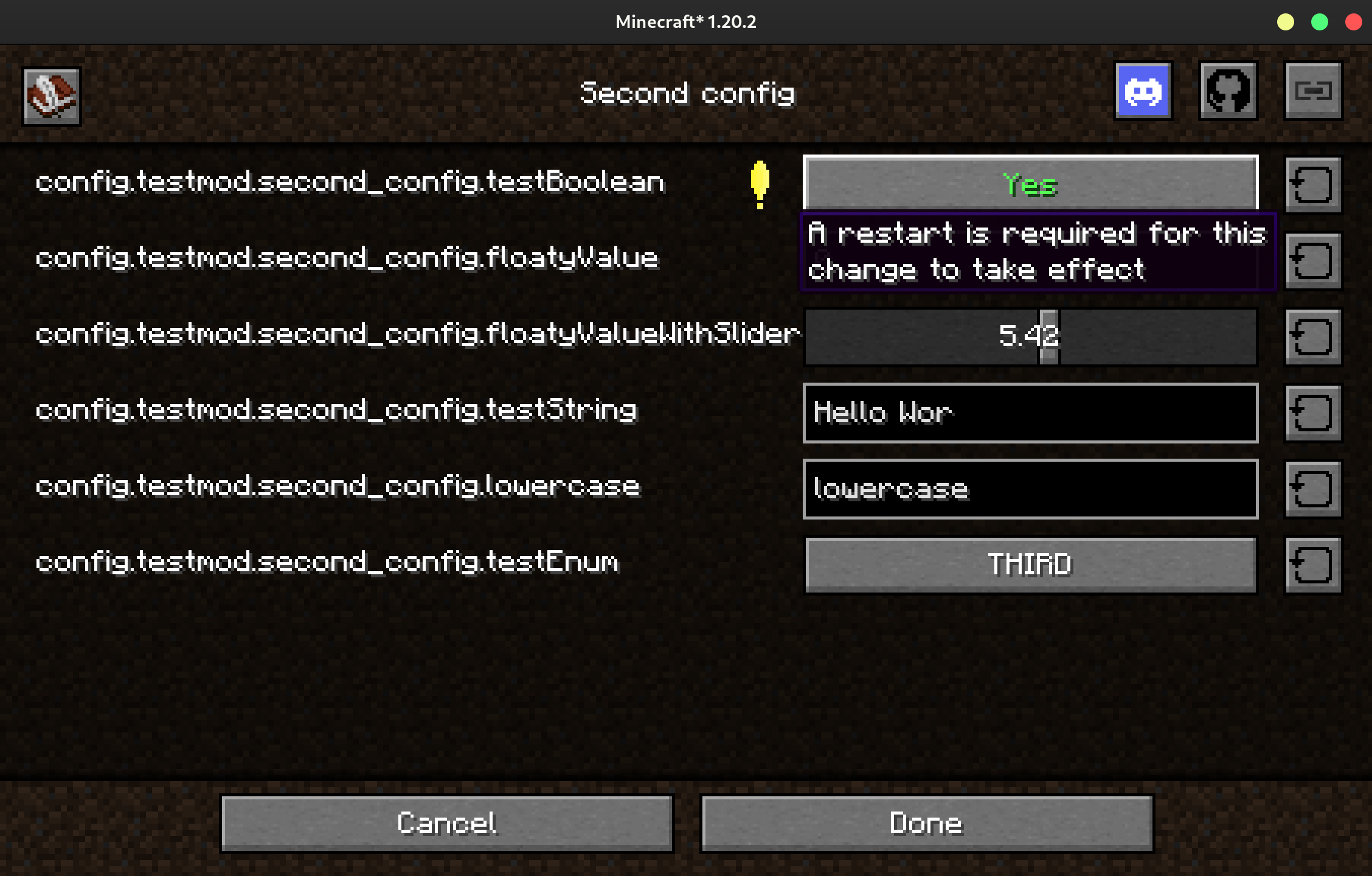
Warning the User That a Restart Will Be Required
Annotating a field with @RestartRequired will warn the user that a restart is
required for the change to take effect when they exit the config screen.
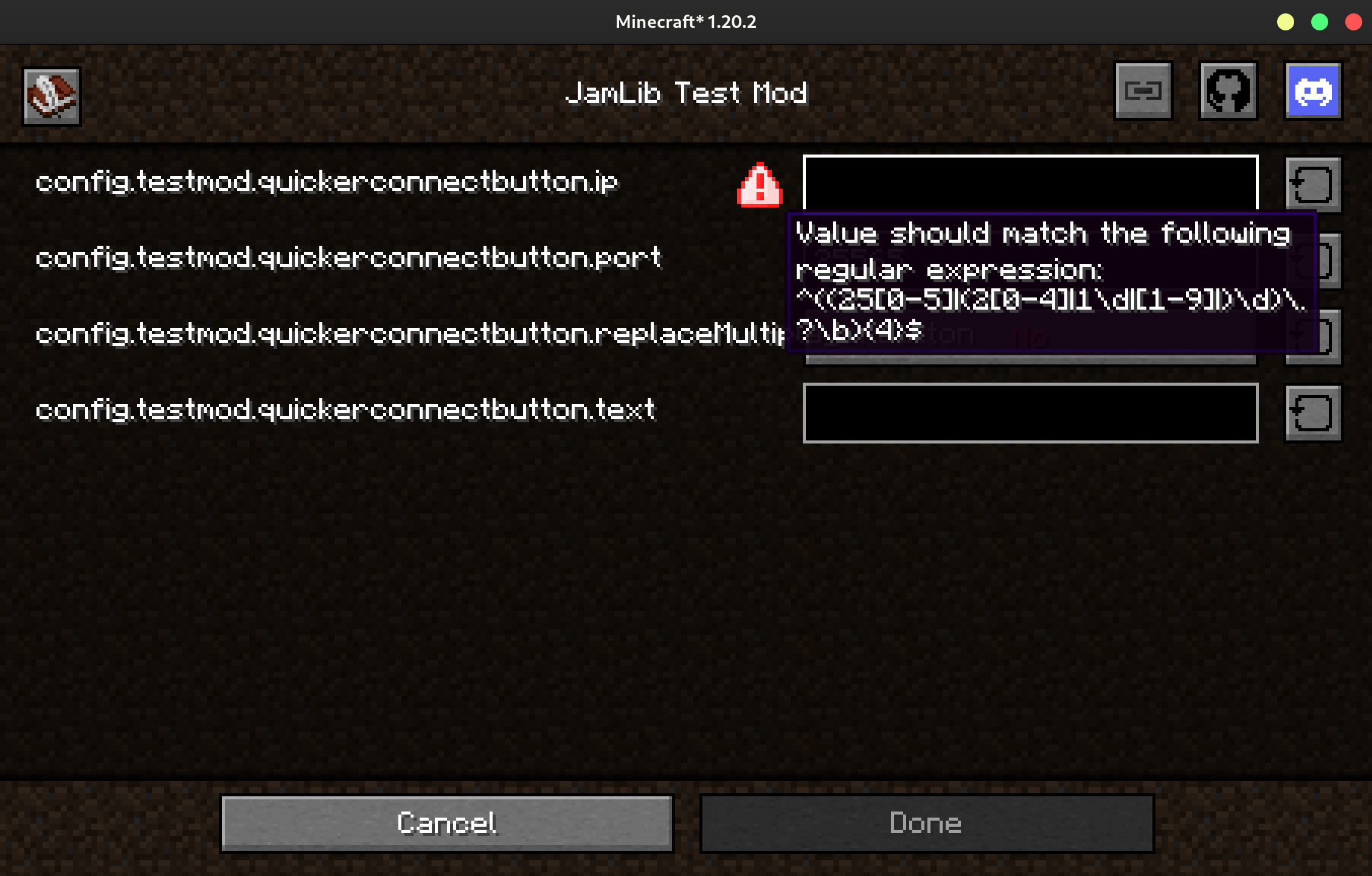
Requiring a String to Match a Regular Expression
Annotating a String field with @MatchesRegex will require that it matches
the regular expression before the user can exit the config screen.
@MatchesRegex("^((25[0-5]|(2[0-4]|1\\d|[1-9]|)\\d)\\.?\\b){4}$")
public String ip = "...";
Requiring a Number to Be Within a Range
Annotating a number field (float, double, int, or long) with
@WithinRange will require that it is within the specified range before the
user can exit the config screen.
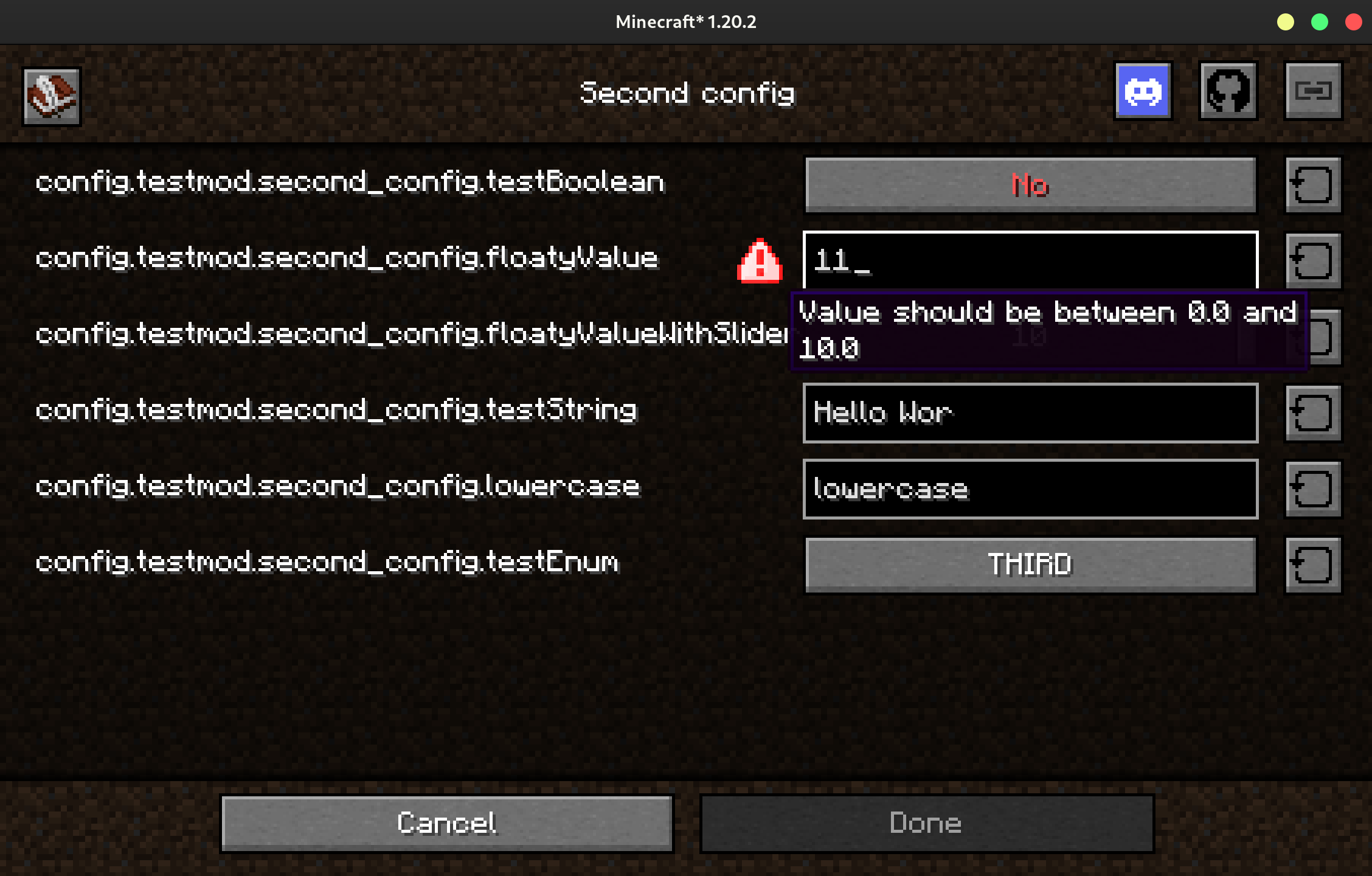
Using a Slider Instead of a Text Field for Numbers
Annotating a number field (float, double, int, or long) with @Slider
will make the config screen add a slider instead of a text field. The field
should also be annotated with @WithinRange.
Adding Comments to the JSON File
You can add a comment to a field in the serialized JSON using the @Comment
annotation provided through the Jankson
transitive dependency.
@WithinRange(min = 0, max = 10)
@Slider
@Comment("This value is used for ...")
public float floatyValue = 3.2F;
Hiding a Config Entry in the GUI
You can hide a config entry in the GUI using the @HiddenInGui annotation. This prevents it from showing in generated config screens, which may be helpful when trying to add a GUI entry using an unsupported type (e.g. lists or maps) which cannot be displayed yet.
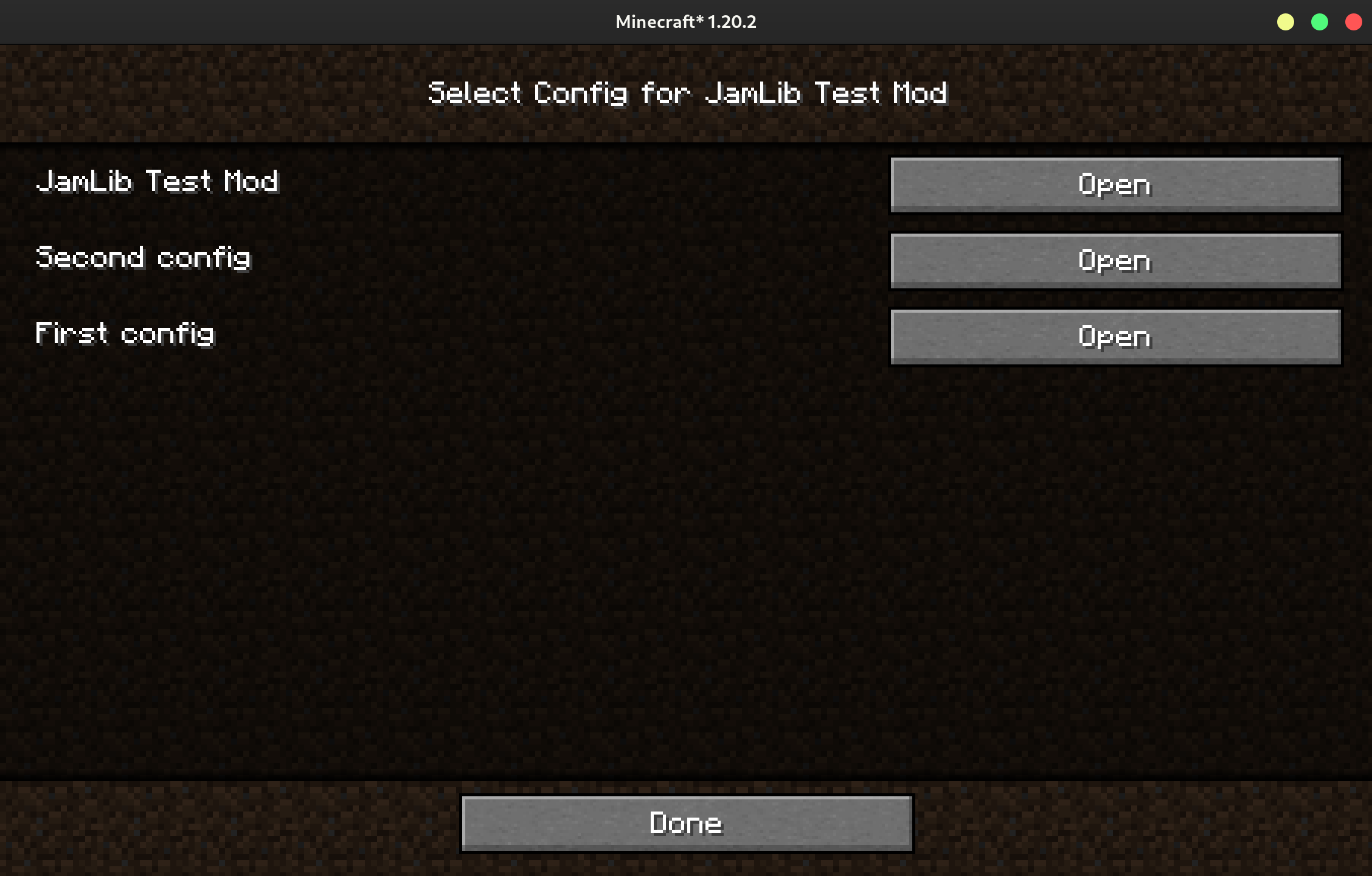
Creating Multiple Configs
A mod can provide multiple configs to the config system, which will then create a screen to allow the user to select which one they would like to edit.
public class YourModInit {
public static final ConfigManager<ClientConfig> CLIENT_CONFIG = new ConfigManager<>(MOD_ID, MOD_ID + "_client", ClientConfig.class); // (1)
public static final ConfigManager<ServerConfig> SERVER_CONFIG = new ConfigManager<>(MOD_ID, MOD_ID + "_server", ServerConfig.class); // (2)
}
- This config file will be saved at
config/MOD_ID_client.json5. - This is just an example, JamLib provides no specific methods to help you with sided configs - it is your responsibility to make sure you are accessing config values on the correct side.
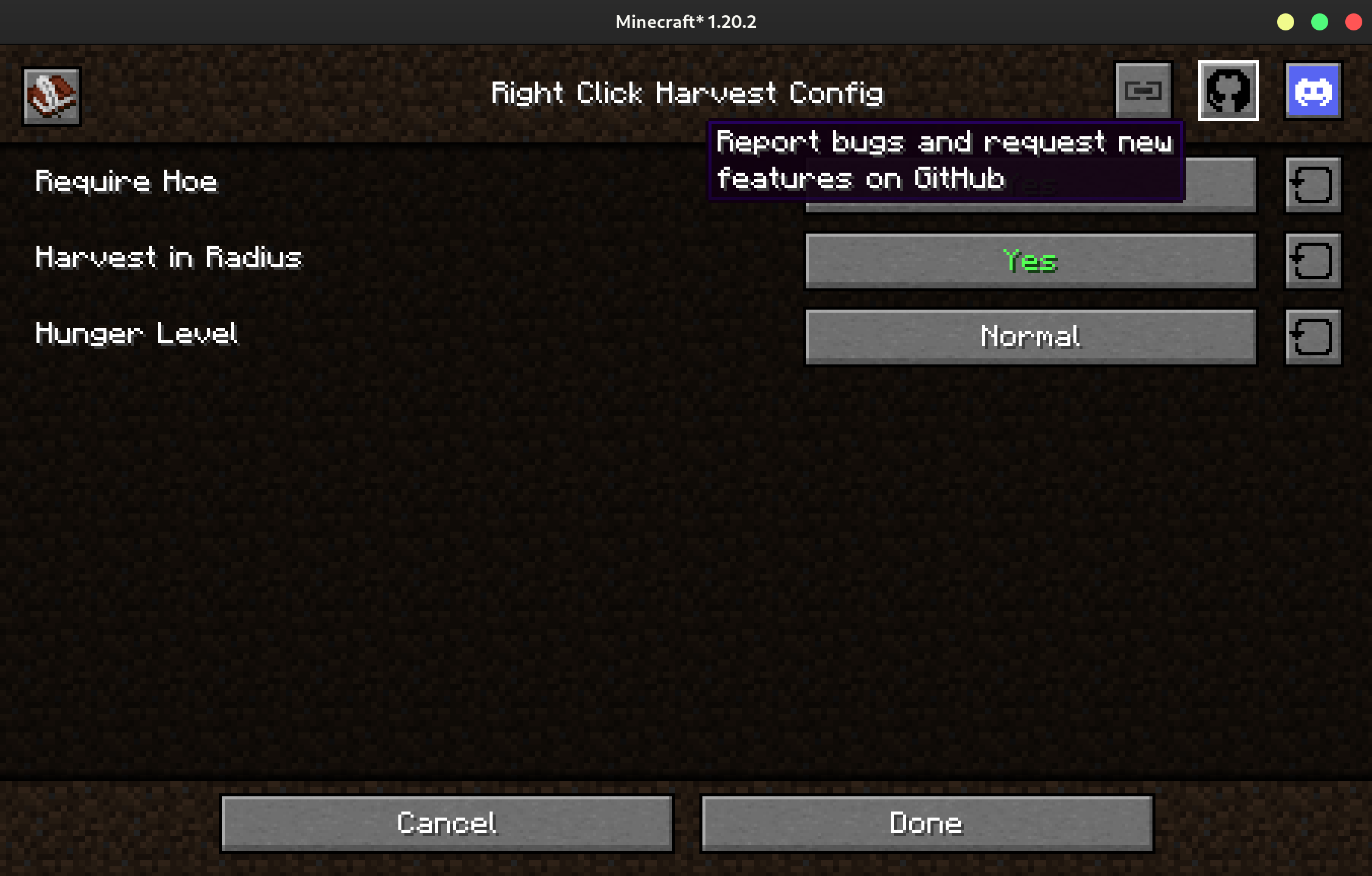
Adding Links
You can add custom links to the top of your config screen if you wish.
public class Config implements ConfigExtensions<Config> { // (1)
// your config fields...
@Override
public List<Link> getLinks() {
return List.of( // (2)
new Link(Link.DISCORD, "https://jamalam.tech/Discord", Component.translatable("config.rightclickharvest.discord")), // (3)
new Link(Link.GITHUB, "https://github.com/JamCoreModding/quicker-connect-button", Component.translatable("config.rightclickharvest.link.github")),
new Link(Link.GENERIC_LINK, "https://modrinth.com/mod/quicker-connect-button", Component.translatable("config.rightclickharvest.link.modrinth"))
);
}
}
- You'll need to implement the
ConfigExtensionsinterface. - It's best to not return too many links here, as they could overflow the screen otherwise.
- JamLib provides
DISCORD,GITHUB, andGENERIC_LINKtextures. You will need to create and provide 16x16 textures if you want any others.
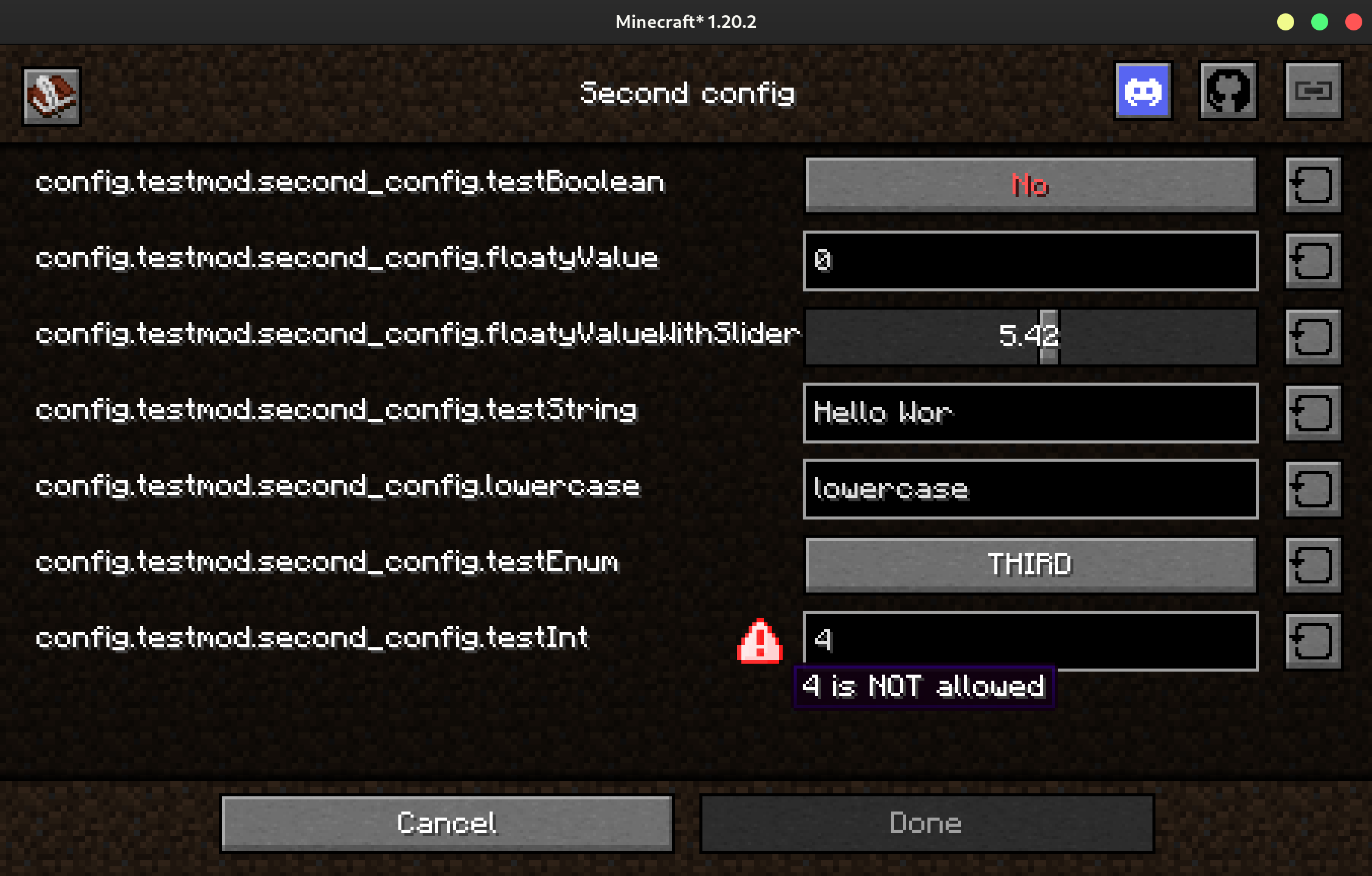
Custom Validation
You can also add a custom validation check that runs when the user is using the config screen to your config.
public class Config implements ConfigExtensions<Config> { // (1)
public int testInt = 3;
@Override
public List<ValidationError> getValidationErrors(ConfigManager<TestConfig> manager, FieldValidationInfo info) {
List<ValidationError> errors = ConfigExtensions.super.getValidationErrors(manager, info); // (2)
if (info.name().equals("testInt") && (Integer) info.value() == 4) {
errors.add(new ValidationError(ValidationError.Type.ERROR, info, Component.translatable("config.testmod.i_dont_like_4"))); // (3)
}
return errors;
}
}
- You'll need to implement the
ConfigExtensionsinterface. - You need to call the default method, as it provides the checks for
annotations such as
@RequiresRestartand@WithinRange. ValidationError.Type.WARNINGis also available. An error prevents the user leaving the screen (without discarding their changes), while a warning just warns them.